Since I wrote previously about Lync 2010 and I stated there that you need Forefront TMG to use as an reverse proxy for Lync components. (You can also use other HLB products such BIG-IP or Netscaler but remember that they don’t have the security capabilities that TMG has, but then again Netscaler and BIG-IP are hardware appliances, so I’m guessing they have a lot better speed than TMG does)
Therefore I thought that everyone could use a quick introduction so what Forefront TMG actually is.
NOTE: UAG Service Pack 1 Update 1? Now support fully Lync so you can use UAG to act as a reverse proxy as well.
But what is Forefront TMG? (for short Threat Management Gateway) and previously known as ISA (Internet Security and Acceleration) Server.
It is a multiple feature product and it includes features like.
Act as an Router, VPN server, NAT server, Proxy Server.
Web caching capabilities.
Application layer and stateful firewall & anti-malware protection.
ISP redundancy (You can for instance have 2 connections to the internet and you can use it for load balancing and failover)
And as many others before me have asked, what is the difference between UAG and TMG?
Well first of TMG is mostly a product to secure your network from outside intrusion, and you would use UAG if you wish to publish internal resources in the most secure manner. UAG is mostly an reverse proxy and SSL-VPN product, but you can use UAG as a firewall as well (it again includes TMG for the firewall part) So in short.
You would use TMG to block unwanted traffic in or to inspect traffic.
You would use UAG to secure corporate access inn.
So this post will be about installing TMG and how to publish Lync web sites via TMG.
Requirements for TMG 2010.
CPU
64-bit, 1.86 GHz, 2 core (1 CPU x dual core) processor.
Memory
2 GB, 1 GHz RAM.
Hard Disk
2.5 GB available space. This is exclusive of the hard disk space required for caching or for temporarily storing files during malware inspection.
One local hard disk partition that is formatted with the NTFS file system.
Network adapters
One network adapter that is compatible with the computer’s operating system, for communication with the Internal network
Operating system
Windows Server 2008
- Version: SP2 or R2
- Edition: Standard, Enterprise or Datacenter
Windows Roles and Features
These Roles and Features are installed by the Forefront TMG Preparation Tool:
- Network Policy Server.
- Routing and Remote Access Services.
- Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services Tools.
- Network Load Balancing Tools.
- Windows PowerShell.
And note that you need to be connected to the internet in order to install Forefront TMG ( Since it needs to download updates etc.)
NOTE: You can check setup log under C:windowstemp
You can download a trial for Forefront TMG from here –> http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/server-cloud/forefront/threat-management-gateway-trial.aspx
Before we start the setup, run the Preparation Tool. This verifies that the computer has all the prerequisites in place.
Here choose that you wish to install TMG services and Management. Click next and the tool will install all the required prerequisites.
Now that we are done with the prerequisites we can continue on with the installation of TMG. Go back to the main setup menu and click Run installation Wizard.

The setup is pretty simple just click next and accept the license terms and choose a default location.
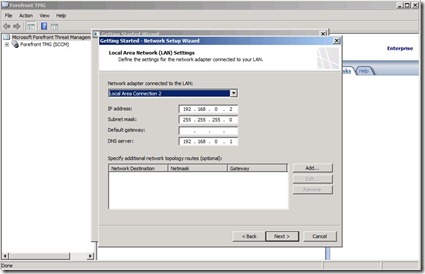
Here you have to add a internal network. Typically you have multiple NIC’s connected to TMG.
In my case “Local Area Connection 2” is my internal network card (If you notice I have a APIPA address. I changed the IP and ran the wizard again, so check that you have the correct IP address set before you continue the installation of course you can change this is in Forefront console afterwards if you wish)
Now after the installation is complete you can open the TMG console from Start –> All Programs –> Forefront TMG –> TMG Management

Before we can start, Forefront has a “Getting Started” wizard that we should take a quick walkthrough before we continue. We can just close it if we want to. B
Press the Configure network settings. Here we can configure how TMG is deployed. In my scenario TMG is the Edge Firewall and local connections to the internet is routed trough the TMG server.
And here again we are faced with configuring what NIC is connected to the internal network.
Next we have to set what NIC that is connected to the internet.
Click next and finish (Now that Forefront has knowledge of what NIC that is connected to the internet and which are connected locally they are now labeled “Internal” & “External”. Which makes it easier for you to setup ACL’s or settings, in case you need to change the NIC on the server. Then you only have to change what NIC is connected to where so you don’t have to change/update all the ACL’s etc.
Now we are back to the getting started wizard, click on “Configure system settings”
In my case I have installed the TMG server as a part of the domain or you can install it in a workgroup, there are both pro’s and con’s to choosing these.
First of if you have TMG a an edge firewall, and it is domain joined if someone manages to compromise your AD domain they might also be able to shutdown the firewall.
Microsoft recommends that you have your TMG servers in another forest with a one-way trust, that way you might prevent the internal forest from being compromised.
Some features requires it to be domain joined, such as the VPN server, in general terms installing TMG in a domain, eases the use of authentication.
Click next and finish.
Now again we are back to the Getting Started Wizard. Click “Define Deployment options” –>

This just goes trough the system settings, Click Use Microsoft Updates (This gives you the ability to update malware definitions and such for forefront.
Here you decide if you wish to Network Inspection System (NIS) and Web Protection w/Malware Inspection and URL filtrering
Network Inspection System is the TMG IPS (Intrusion Prevention System) which is signature based. So before It can start protecting your network from unwanted traffic you need to download NIS signatures.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd441019 (This enables traffic to be inspected for exploits of Microsoft vulnerabilities)
Another thing you can do is use metasploit to test your network for known exploits and see if Forefront triggers ( But more about that in a later post)
URL filtering enables you do deny/grant access to web sites based on URL categories such as (porn,drugs etc)
(Customer Feedback) As I have stated before Microsoft actually uses this data so it should be enabled ![]()
Click Next and now you are finished with the setup, by default the setup marks the “Run the web Access Wizard” after you click close.
So if you don’t want to do any changes there just remove the mark and click close.
We can take a quick look at the Web Access Wizard as well ![]()

First of if we wish to have TMG setup default rules that block access to malicious URL we can enable that here. Click next and lets add a blocked web destination.

In my case I’m going to add vg.no.
You can add a * as a wildcard after the URL.
For instance http://microsoft.com/*

Add that to a destination category, click OK.
You can also create overrides (Here you can add active directory users that have unrestricted web access, regardless of ACLs) Click next

Here the malware inspection settings, comes in. Choose Yes here to enable malware inspection.
Here you can choose if you wish that users can enable https connections to sites. In my case I choose “Do not allow” This will do so the users cannot login to sites that require HTTPS. Click next

Now we come to the web cache configuration, this will allow TMG to cache frequently requested web objects in memory and on disk in order to improve web browsing performance and to reduce bandwidth utilization. So when a user tries to browse to a site, TMG will automatically try to fulfill the request from the cache. If the content is not in the cache, it will make the request to the webserver as normal. We will go more in on the different options on caching later in the post. What I did here is add a local cache on the server with a total of 2000 mb. After that is done click Next.
And finish!
We are now back to the main console.

As you can see here TMG has now applied the default rules in the wizard. IT has created 4 rules.
1 to block HTTPS traffic (Which we defined in the wizard)
2 to block web destinations to VG Nett
3 Allow web access for all users
4 The last rule which is a implicit deny all.
These rules are always proceeded from down –> up, so by default all traffic is blocked, but it allows for regular HTTP traffic (Since HTTPS traffic is blocked as the final rule)
You have the ability to move rules up and down so you can alter the processing. And as you can see on the top even if the policy are visible there aren’t active. We have to click “Apply” first.
And you can also see in what direction the traffic is being blocked.
Now lets do the Lync part. (This guide is for a standard Lync Edition)
First of we need to use a reverse proxy to publish Lync https content.
- Enabling external users to download meeting content for your meetings.
- Enabling external users to expand distribution groups.
- Enabling remote users to download files from the Address Book service.
- Accessing the Microsoft Lync Web App client.
- Accessing the Dial-in Conferencing Settings webpage.
- Accessing the Location Information service.
- Enabling external devices to connect to Device Update web service and obtain updates.
- Enabling mobile applications to automatically discover mobility URLs from the Internet.
First of, right-click Firewall Policy, point to New, and then click Web Site Publishing Rule.

In the web publishing rule name (Type something with a good description)
Here you set it to allow. Click next –>

Choose Publish a single web site or load balancer, click next –>

On the Server Connection Security page, select Use SSL to connect to the published Web server or server farm.
Click Next –>
Here type the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the internal web farm that hosts your meeting content and Address Book content in the Internal Site name box.
If you don’t have DNS in the perimeter network you can add a IP address in the other menu. Click next –>

On the Internal Publishing Details page, in the Path (optional) box, type /* as the path of the folder to be published.

On the Public Name Details page, confirm that This domain name is selected under Accept Requests for, type the external Web Services FQDN, in the Public Name box.

On Select Web Listener page, click New to open the New Web Listener Definition Wizard.
On the Welcome to the New Web Listener Wizard page, type a name for the web listener in the Web listener name box (for example, LyncServerWeb).

On the Client Connection Security page, select Require SSL secured connections with clients.

On the Web Listener IP Address page, select External, and then click Select IP Addresses.
On the External Listener IP selection page, select Specified IP address on the Forefront TMG computer in the selected network, select the appropriate IP address, click Add.
On the Authentication Setting page, select No Authentication.
On the Authentication Delegation page, select No delegation, but client may authenticate directly.
On the User Set page, click Next. Click next and finish.
Then click Apply in the main menu.
Now in the Firewall Policy window you will now get a new policy named “Lync” in my case.
Right click on it and press properties.
Go to the From tab, choose “Anywhere” and click Remove.
Then press the Add button and choose External.
Next click on the bridging tab and select the Redirect request to SSL port check box and then specify port 4443.
Click Apply, OK.
Then click Apply in the Firewall console.
Now you have published Lync https roles via TMG.
You can read more about publishing Lync sites via Reverse Proxy here –> http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/gg398069
We have just scratched the surface here for what Forefront TMG has to offer. Unlike its hardware firewall buddies, it operates in the highest levels of the OSI layers, and has more specific application layer protection that hardware appliances don’t have.
Many companies today have a two-tier solution, they have a stateful firewall in the front and a application layer firewall in the back. The purpose of the stateful firewall is to make sure that only fully established connections are allowed in, it doesn’t care if there is a malicious traffic that is being transmitted is just knows that its established a connection and that the three-way handshake is verified (It mostly cares about layer 4 in the OSI model, and its much faster then TMG, this is useful for instance stopping TCP syn flood ddos and general noise) after that the traffic is then forwarded to TMG which handles all the malware inspection and higher level inspections.




























Hello just wanted to give you a brief heads up and let you know a few of the images aren’t loading properly. I’m not
sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different web browsers and both show the same outcome.