NOTE: This post is just a little google translation of my previous post written in Norwegian J
Today, there are a wealth of options when it comes to backup, the focus has shifted to a large extent from being able to backup only physical machines to be able to back up the physical, virtual and applications located on the machines (like SQL, Mail, IntraWeb, business applications) solutions have higher demands on them in terms of handling large amounts of data, while it should be easy to use and be quick to be able to restore data.
There are many different suppliers of backup software on the market, to name a few:
Altoros http://www.altaro.com/hyper-v-backup/
Acronis http://www.acronis.com/backup-recovery/enterprise.html # agent-windows
Microsoft DPM http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh758173.aspx
Dell Appasure http://www.appassure.com/
Symantec Backup Exec 2012 http://www.symantec.com/products/data-backup-software
IBM TSM http://www-142.ibm.com/software/products/us/en/tivostormana/
Then there is Veeam:
The difference with Veeam In relation to the other manufacturers is that they focus only on the virtual layer, thus you will get a tailored solution that is only geared towards virtual infrastructure.
Veeam has also recently launched a new version of its main Backup and Replication in version 6.5, which introduces some new functionality and support for new products, they include come with support for Windows Server 2012 and VMware vSphere 5.1, which means that they were first with support for these new products. For those who are not so familiar to Veeam, so you can read a bit more about them here -> http://www.veeam.com/company/about.html?ad=menu
Veeam has the following software to its portfolio:
Veeam Backup and Replication (Which is the main product of Veeam, used for backup and replication of virtual machines (VMware and Hyper-V) plus much more. It also has its own tools for backup and recovery to
Exchange, AD and SQL) sounds as a regular backup product, but it has some features that make it unique compared to the competition I get into that later. You can read more about the product here http://bit.ly/SdvvAF
Veeam ONE (Which is a complete monitoring tools to monitor Hyper-V and VMware, it also has built-in reporting tools)
You can read more about it here http://bit.ly/TuYqU8
Veeam Management Pack (which is a by-product (Management Pack) for System Center Operations Manager provides full monitoring of your VMware infrastructure Operations Manager)
Previously called nWorks Management Pack. You can read more about it here http://bit.ly/Rtb5Gk
In addition, they also have other products:
Veeam Backup Free Edition (Which is a minimal version of Backup and Replication is mostly used to make copies of virtual machines and compressing them via VeeamZIP)
Veeam One Free Edition (Is a minimal version of Veeam One and have some restrictions on how long it can store data)
Backup and Replication consists of three components
Proxy Server: this is that makes the job of extracting data from the server as it should be backed up and put this in a repository.
Backup Server: Administration server, here you enter the backup jobs that you want and run. All of the work and statistics are stored in an SQL database connected to the server.
Repository: This is where the backup data is added.
So mainly it is the Proxy server that goes in and retrieves data from the server and passes it on to Backup Repository. Surely, you notice that a backup job takes too long; you can easily add more proxy servers (when Proxy server works very CPU intensive)
I’ll show how to define different proxy servers for different jobs in a next post.
However, when to reveal Bottlenecks are four things to look for. NB: Sure Veeam reveals when there is a bottleneck, the lower the “speed” of the rest of the components to the speed that the weakest link handles.

1: Hyper-V host (Much to read and write to the disk?)
2: Proxy server (Is the CPU reaches max?)
3: Network (Has it reached its maximum bandwidth?)
4: Target repository (Much to read and write to the disk?)
Other components:
Enterprise Backup Server: Possibility to manage multiple backup servers, it also allows you to search through backups for individual files
Backup Search: User MOSS Integration Services on a Microsoft search server for faster and be able to search through the data.
The architecture of Hyper-V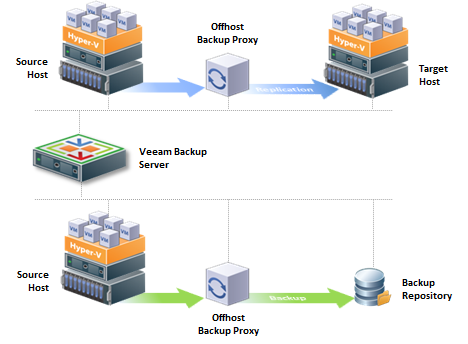
Basically it will be installed a proxy sever on Hyper-V host, you certainly need to take the load away from the Hyper-V host, you must have a server that is set up as Offhost Data Proxy
(This requires a server that is installed with Hyper-V VSS due and should be the same Hyper-V version for it to backup)
The architecture of Vmware
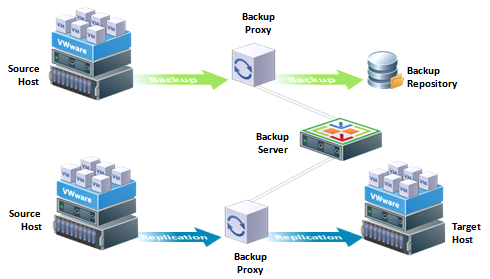
For its part, Vmware hasnothing that is installed on the host, you must set up a separate Windows server running as the Backup Proxy (This server should have access to the same storage that Vmware host has)
This server can also be a virtual machine running on VMware but this requires that the server HotAdd access to VMs on Datastore)
Supported systems:
Hypervisor
Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2008 R2 SP1
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 with Hyper-V
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 with Hyper-V
vSphere 5.0, 5.1
Management Server (not required)
If you want to backup against VMM it requires the installation of the VMM console on the backup server)
Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager 2008 R2 SP1
Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager 2012
You can read more about the recommendations regarding hardware and supported systems here ->
http://bit.ly/VSqfn0
Installation:
The installation of Veeam requires that also installed
. Net Framework 4.0
A SQL Server either locally or on another server.
If you do not have any of the parts will Veeam installation install both (though a SQL Express version of 2008 R2)
Installation is very simple and streamlined
Enter the license file you have received.

Management Console (Is Backup server with components)
Catalog Service (Is responsible for indexing the VM OS files)
PowerShell snap-in (Provides PowerShell commands that can be used to automate backup akviteter via script)

If you do not have any SQL servers available, select local setup (This installation will set up a SQL Express 2008R2)
The application supports most versions of MSSQL
• Microsoft SQL Server 2005 (Full and Express Edition)
• Microsoft SQL Server 2008 (Full and Express Edition)
• Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 (Full and Express Edition)
• Microsoft SQL Server 2012 (Full and Express Edition)

Here you must specify a user that has full database permissions on the database. The same users will be automatically granted “Log on as a service” privilege on the server.
So here, it is advisable to use a least-privilege user.

Then, just click Next and then install.
B & R can now be launched from the desktop or the Start menu.

Before we start adding Hyper-V servers and configure backup is important that we go through the setup on the server to the configuration options available there.

It is mainly divided into 5 tabs.
Backup & Replication (Here you define backup and replication jobs, getting all the backups you have set up)
Virtual Machines (Lists all virtual machines that are connected in the Veeam)
Files (Lists the files on the physical Host)
Backup Infrastructure (Here you define which servers will be Proxy servers, which server will be the repository and the servers that are managed by Veeam)
History (Lists all jobs that have been run through Veeam)
In addition, you have an additional menu when you click on the Session Tools button at the top left, here you can access the PowerShell module, opportunities to put
user access, define traffic throttling, backup configuration and set up notification (SNMP and e-mail) I’m going to come back a little PowerShell and examples you can use later.
Under “Help” menu, you have the opportunity to look at the license is tied up in the Veeam server and the ability to change the license.
When we add a new virtualization host, we go to Virtual Machines, right-click on
Microsoft Hyper-V to select Add Server.
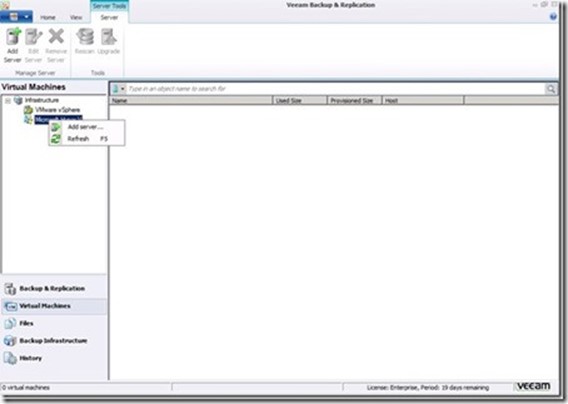
Add the IP address of the host
Now we have the choice whether we want to link it to the Virtual Machine Manager or standalone / cluster Hyper-V host. In this context, I am going to choose Hyper-V host,
but you want to use it against VMM must have VMM console installed on the Backup Server.

At the same time PowerShell on VMM server must be set to Remote Signed to Veeam server access to run PowerShell commands on the VMM host.
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
Once we have selected Hyper-V and goes on we are asked to add a user (This must have local administrator rights on the Hyper-V server)
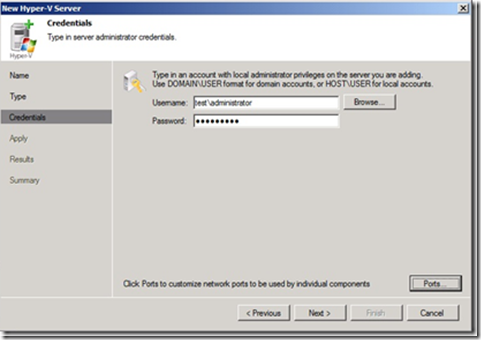
Then you will get the components that will be installed on the Hyper-V server and the number of concurrent jobs Hyper-V host can do.
Hyper-V hosts with multi-core processors can handle multiple simultaneous tasks. For example, for 4-core CPU, it is recommended to specify a maximum of two simultaneous tasks,
for 8-core CPU – 4 simultaneous tasks. Nevertheless, when you define the number of concurrent tasks, you should keep in network traffic flow in your virtual infrastructure.
Transport component is responsible to shuffle data from the Hyper-V server to a repository (Proxy component)
Hyper-V Integration (Is responsible for managing VSS communication with VMs, the Service also distributes a driver that handles the change block tracking for Hyper-V.)
When it is finished installing, you will get a list of all VMs that are attached to the current Hyper-V server.

If you got any problems with installation, check the Event log -> Application or under Log folder to Veeam
Also check that the services on Hyper-V server is running properly.

Once you have verified that it is operational, we can add a backup job.
Go to Backup and Replication -> Right click on jobs and select Backup

Give the job a descriptive name and a good description.

Select Add from the right list and select the VM (Alternatively VM host) that will be backed up.
(You select Exclusions VM that should not be backed up or possibly the disk Veeam will not backup)

Under Storage decide which proxy to use to retrieve the backup and the repository will be stored on VMs.

Off-host (so the proxy job running on its own dedicated server with transport role installed)
On-host (So Hyper-V server running backup job to backup directly shipped to a repository)
You can also add the failover (If an Off-host proxy does not respond as an on-host proxy take over the job)
But I will nevertheless recommend that you add a new off-host proxy server that can be used to relieve the Hyper-V server.

So when we start a backup job in this way.
1. Veeam Backup & Replication triggers a snapshot of the required volume of production Hyper-V host.
2. The created snapshots are divided from the production server and mounted on offhost backup proxy.
3. Veeam agent running on a backup proxy using a mounted volume snapshot to extract VMs, VMs processed on the proxy server to be copied to the repository.
4. When the backup is complete, the snapshot is removed from the backup proxy.
If we click on the advanced button where you have a number of choices.
Backup

* Reversed Incremental
(Basically, when you take an incremental backup means that you take a copy of all the data that has changed since the last backup)
One takes a full backup one time in a week, so you take a backup of the changes that are made every day. So in this case here certain you want a full backup from Friday.
When you restore
Sunday + Monday + Tuesday + Wednesday + Thursday + Friday.
With Reversed Incremental changes are “sprayed” in the VBK file to restore it to the latest state of the VM. It also creates a reverse
incremental backup file (. VRB) contains data blocks that are replaced when full backup file is restored.
Therefore, the last restore point is always a full backup, and it will be updated after each backup cycle. With reversed incremental backup can immediately
restore a VM to the latest backup additional processing, because the last restore point is a full backup file.
If you need to restore a VM to a specific point in time, Veeam Backup & Replication applies the necessary. VRB files. VBK file to get the desired recovery point.
* Enable Full Synthentic
Veeam creates a new full backup of the backup data is stored from before.
* Perform Active Full
Veeam will bring out a new full backup of VMs.

Storage
Enable inline data deduplication:
Means of Veaam will deduplicate data as they moved to the backup repository (Note that this requires more CPU)
Compression:
• No Compression is recommended if you are using storage devices with hardware compression and deduplication tool to store backups.
• dedupe-friendly compression is an optimized compression level for very low CPU usage. It is recommended if the backup proxy does not meet the minimum system requirements, and you do not want to load it heavily.
• Optmial Compression is the recommended compression level gives the best compromise between the size of the backup file and the time of the backup.
• Extreme Compression and the smallest size of the backup file but reduces backup performance. We recommend that you run the backup proxies on computers with modern multi-core processors (6 cores recommended) if you intend to use the best compression.
Storage Optimizations:
* Local target. This option is recommended if you plan to use SAN, DAS or local storage as a target. SAN identifies larger blocks of data, and therefore can process large amounts of data simultaneously. This option provides the fastest backup, but reduces deduplication – the larger the data block, the lower the chance to find an identical block.
• LAN target. This option is recommended for NAS and on-site replication. It gives a better dedupe and reduce the size of an incremental backup file.
• WAN target. This option is recommended if you plan to use the WAN for offsite backup. Veeam uses small data blocks, which involves significant processing overhead, but results in the maximum dedupe and the smallest size incrementelle files.
Deduplication views block for block to see if there are any identical block files, so instead of saving redundant data will instead refer to the second block file.

Compression looks at the file file, to see if the file contains a number of duplicate data. For example, a JPG image that contains the value (red pixel, red pixel, red pixel, red pixel …….. red pixel) Instead of saving this several times you can compress this
by saying (red pixel x 249) So therefore, one could get saved large amounts of data to compress such files.
Before

After

Notifications:
Here we can set up notifications to an email address or SNMP when a job is completed / errors / alerts
Hyper-V

* Enable Hyper-V guest quiescence (Certainly, where for one reason or another can not make use of VSS for backup of VMs must check here) Basically, Veeam then put VMs In Pause while the backup.
* Take Crash Consistent Backup (Of course we want the VMs to be online while taking backup (While “Enable Hyper-V guest” is enabled) must tick here)
The difference between a regular backup (usually called an application-consistent backup) and a crash consistent backup is. In a nutshell, creates crash consistent backup a snapshot that when restored, creating a virtual machine similar to the one that had the power suddenly turned off.
Snapshot will return the virtual machine’s operating system to its pre-crash condition, but does little to preserve the consistency of open files or transactional databases that reside on it. On the other hand, an application-consistent backup ensure that all database transactions are completed and all disk transactions are conducted before a snapshot. This ensures data integrity of open files and databases on each backup.
* Changed Block Tracking
Changed block tracking will drastically improve the resources used and time spent on incrementally backups, certainly one can use CBT hypervisor will keep track of what’s changed since last time so that it becomes easier for Veeam to extract the changed data blocks.
Advanced
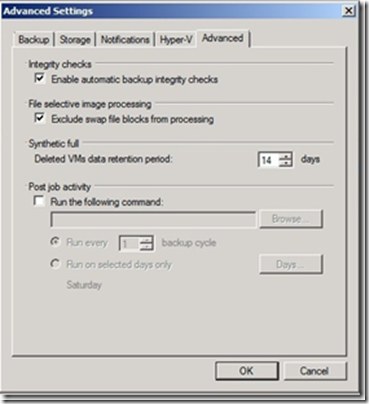
* Integrity Checks
Will check the integrity of a backup so that you do that you are left with corrupt data on a repositrory.
* File Selective Image Processing
Here you determine whether you should backup the swap file on a VM, swap files on Windows machines is very dynamic and changing very often even if a VM does not. Surely you do not want to backup this you activate this.
* Synthetic Full
Here you determine how long to keep a VM after it is optionally deleted from your infrastructure.
* Post Job activity
Optionally you can create a script that can be used to write the backup to tape as
After we finished there, we go back to the job setup.
* Enable application-aware image processing
As I mentioned earlier this will perform an application-aware backup.
* Enable guest file system indexing
If you want to index files in the guest VM to backup, check for this. Veeam will perform file indexing and enabling you to perform searches for VM guest OS files via Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager web interface.
Next is to create a schedule for when to backup
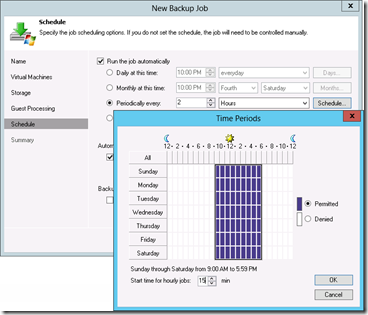
after that is done you can run the backup job.

Now you see the details of the job you will see where the bottleneck is on the job and how much data is processed.
In this case, the Hyper-V server that has too much strain before that makes it go so smoothly.

At the same time I have enabled ordinary deduplication and compression, which allows it saves a lot of space on the repository.